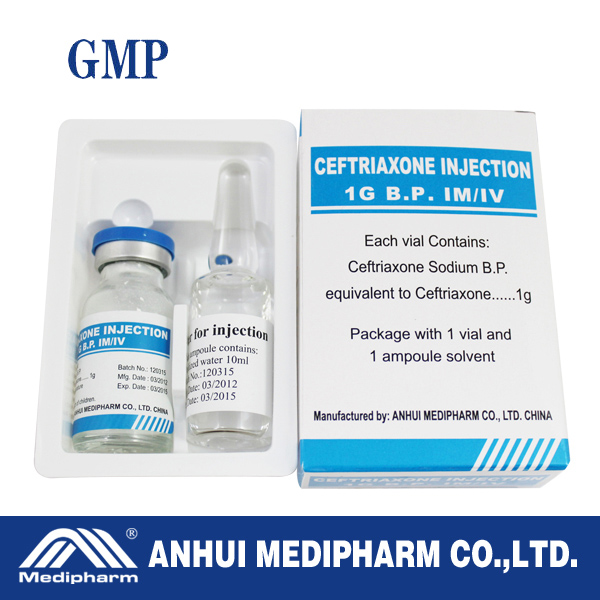
| Message: | Indications:
Ceftriaxone is often used (in combination, but not direct, with macrolide and/or aminoglycoside antibiotics) for the treatment of community-acquired or mild to moderate health care-associated pneumonia. It is also a choice drug for treatment of bacterial meningitis. In pediatrics, it is commonly used in febrile infants between 4 and 8 weeks of age who are admitted to the hospital to exclude sepsis.
Contra-indications:
Ceftriaxone is contraindicated in neonates if they require (or are expected to require) treatment with calcium-containing IV solutions, including continuous calcium-containing infusions such as parenteral nutrition because of the risk of precipitation of ceftriaxone-calcium.
Adverse Effects:
Hypoprothrombinaemia and bleeding are specific side effects. Haemolysis is reported. Biliary sludging is another known though rare adverse effect which occurs primarily in neonates.
Drug Interactions:
Ceftriaxone can interact with a number of medicines. Drugs that can interact with ceftriaxone include, but are not limited to, the following: Warfarin, Probenecid, Sulfinpyrazone, Calcium.
Use in Pregnancy and Nursing Mothers:
Ceftriaxone is excreted into human milk in small amounts. Ceftriaxone is considered compatible with breast-feeding by the American Academy of Pediatrics. The manufacturer recommends that caution be used when administering ceftriaxone to nursing women.
Treatment/antidote in The Event of Overdose:
In the case of overdosage, drug concentration would not be reduced by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. There is no specific antidote. Treatment of overdosage should be symptomatic.
Storage instructions:
Store below 25 degrees celsius. Protect from moisture. Keep out of reach of children.
Validity: Three Years
|
 my account
my account
 log out
log out
 my account
my account
 log out
log out